ATDM A-Temporal Diffusion Model (Semeion©)
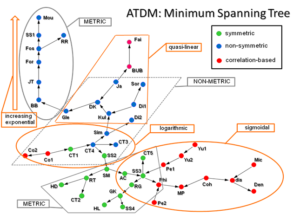
Atemporal Target Diffusion Model (ATDM) is a recently proposed algorithm that has been developed to detect the dependencies among pairs of variables in large datasets, whilst also taking approximate account of their higher order relationships with other variables. The results of an ATDM analysis are given in terms of a Minimum Spanning Tree (MST), which allows one to have simple graphical visualization and inspection of data relationships and patterns.
Performance of the ATDM method was investigated and discussed towards the most classical methods of data analysis by means of some datasets targeted to exploratory data analysis.
An example: 44 binary similarity coefficients (years 1884 – 2012).
100,000 random contingency tables (random combinations of the frequencies a,b,c and d), with the constraint that frequency sum (p) has to be 1024.
The ATDM approach allows the identification of further patterns and relationships among the similarity indices, i.e., metric and non-metric coefficients along with their functional shape (see figure below):
[1] G. Ferilli, P.M. Buscema, P.L. Sacco
The Non-Linear Relationship between scientific production and National States’ Journal,Advances in Computer Science and Engineering
Vol. 9, Number 1, 2012, Pages 47-65, Pulshpa, India.
[2] R. Todeschini, V.Consonni,H.X iang, J.Holliday, P.M. Buscema, P.Willett
Similarity Coefficients for Binary Chemoinformatics Data: Overview and Extended Comparison Using Simulated and Real Data Sets
J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 2884−2901, dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci300261r.
