AutoCM – Auto Contractive Map (Semeion©)
AutoCM is a family of adaptive algorithms (ANNs) able to detect hidden information at high order of association in any dataset.
AutoCM neural network was designed by P.M. Buscema in 1999 and its learning law was improved up to 2013. The software implementing AutoCM is developed by Semeion Research Center in Rome and it is available free for academic applications.
AutoCM has an architecture based on three layers of nodes: an input layer that captures the signal from the environment, a hidden layer which modulates the signal within the network, and an output layer which returns a response to the environment on the basis of the processing that occurred. The three layers have the same number N of nodes. The connections between the input layer and the hidden one are mono-dedicated, whereas those between this hidden layer and the output layer are completely connected. Each connection is assigned a weight: vi for connections between the ith input node and the corresponding hidden node, wi,j for those between the generic jth node of the hidden layer and the ith node of the output layer.
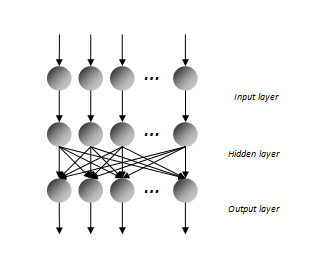
Architecture of the AutoCM neural network
For the training, datasets are scaled between zero and one and all weights initialized beforehand to the same positive value close to zero. Then the network must undergo a series of epochs. In each of them, all the input patterns must be presented one after another to the network, and a calculation made for the appropriate equations with the corresponding output value and a measure of error with respect to the desired value. In accordance with the principle of batch update, the corrections accumulated for an epoch must be applied at the end.
AutoCM was validated in many applications on real data in medical field and in crime profiling, with specific peer review papers.
References
[1] P.M.Buscema (ed),
Squashing Theory and Contractive Map Network
Semeion Technical Paper #32, Rome, 2007.
[2] P.M.Buscema
A novel adapting mapping method for emergent properties discovery in data bases: experience in medical field
in “2007 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC 2007)”. Montreal, Canada, 7-10 Ottobre 2007.
[3] P.M.Buscema, E.Grossi
The Semantic Connectivity Map: an adapting self-organizing knowledge discovery method in data bases. Experience in Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Int. J. Data Mining and Bioinformatics, Vol. 2, No. 4, 2008.
[4] P.M.Buscema, E.Grossi, D.Snowdon, P.Antuono
Auto-Contractive Maps: an Artificial Adaptive System for Data Mining. An Application to Alzheimer Disease
in Current Alzheimer Research, 2008, 5, 481-498.
[5] P.M.Buscema, R.Petritoli, G.Pieri, P.L.Sacco
Auto Contractive Maps
Semeion Technical Paper n. 32, October, 2008
[6] P.M.Buscema, C.Helgason, E.Grossi
Auto Contractive Maps, H Function and Maximally Regular Graph: Theory and Applications
Special Session on “Artificial Adaptive Systems in Medicine: applications in the real world, NAFIPS 2008 (IEEE), New York, May 19-22, 2008.
[7] C.Helsagon, P.M.Buscema, E.Grossi
Is Information Being Denied to the Scientific Community by the Reductionist Approach to Data Analysis in Stroke Related Clinical Trials ?
NAFIPS 2008 (IEEE), New York, May 19-22, 2008
[8] K.M.Momary, N.L.Shapiro, L.D.Brace, S.Shord, E.Grossi, M.A.Viana, C.M.Helgason, E.A.Nutescu, L.H.Cavallari
Influence of Cyclooxygenase-1 Genotype on ex vivo Aspirin Response in Patients at Risk for Stroke?
Cerebrovascular Disease, PubMed, Vol.27, N°6, 2009
[9] F.Licastro, E.Porcellini, M.Chiappelli , P.Forti , P.M.Buscema et al.
Multivariable network associated with cognitive decline and dementia
in Neurobiology of Aging, Vol. 1, Issue 2, February 2010, 257-269.
[10] P.M.Buscema, E.Grossi (eds)
Artificial Adaptive Systems in Medicine
Bentham e-books, 2009, 25-47.
[11] P.M.Buscema, P.L.Sacco
Auto-contractive Maps, the H Function, and the Maximally Regular Graph (MRG): A New Methodology for Data Mining
Chapter 11, in V.Capecchi et al. (eds.), Applications of Mathematics in Models, Artificial Neural Networks and Arts, Springer, New York. 2010.
[12] P.M.Buscema, P.L.Sacco
An Artificial Intelligent Systems Approach to Unscrambling Power Networks in Italy’s Business Environment
Chap.12, in V.Capecchi et al. (eds.), Applications of Mathematics in Models, Artificial Neural Networks and ArtsSpringer, New York, 2010.
[13] E.Grossi, G.Tavano Blessi, P.L.Sacco, P.M.Buscema
The Interaction Between Culture, Health and Psychological Well-Being: Data Mining from the Italian Culture and Well-Being Project
J.Happiness Studies, Springer, 2011.
[14] F.Licastro, E.Porcellini, P.Forti, P.M.Buscema, I.Carbone, G.Ravaglia , E.Grossi
Multi factorial interactions in the pathogenesis pathway of Alzheimer’s disease: a new risk charts for prevention of dementia
Immunity & Ageing 2010, 7 (Suppl 1): S4.
[15] T.Gomiero, L.Croce, E.Grossi, L.De Vreese, P.M.Buscema , U.Mantesso, E.De Bastiani
A Short Version of SIS (Support Intensity Scale): The Utility of the Application of Artificial Adaptive Systems
US-China Education Review A 2 (2011) 196-207.
[16] P.M.Buscema, F,Newman, E.Grossi, W.J.Tastle
Application of Adaptive Systems Methodology to Radiotherapy
in NAFIPS 2010, 12-14 July, Toronto, Canada.
[17] P.M.Buscema, S.Penco, E.Grossi
A Novel Mathematical Approach to Define the Genes/SNPs Conferring Risk or Protection in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Based on Auto Contractive Map Neural Networks and Graph Theory
Neurology Research International, Volume 2012, August 2012.
[18] P.M.Buscema, E.Grossi
The concept of individual semantic maps in clinical psychology: a feasibility study on a new paradigm
in Quality and Quantity, August 04, 2012.
[19] P.M.Buscema, F.Newman, G.Massini, E.Grossi, W.J.Tastle, A.K. Liu
Assessing Post-Radiotherapy Treatment Involving Brain Volume Differences in Children: An Application of Adaptive Systems Methodology
chapter 1, pp 1-23, in W.J.Tastle (ed.), Data Mining Applications Using Artificial Adaptive Systems, DOI 10.1007/978-1-4614-4223-3_1, # Springer Science+Business Media New York 2013.
[20] M.Gironi, M.Saresella, M.Rovaris, et al
A novel data mining system points out hidden relationships between immunological markers in multiple sclerosis
Immunity & Ageing 2013, 10:1 doi:10.1186/1742-4933-10-1.
